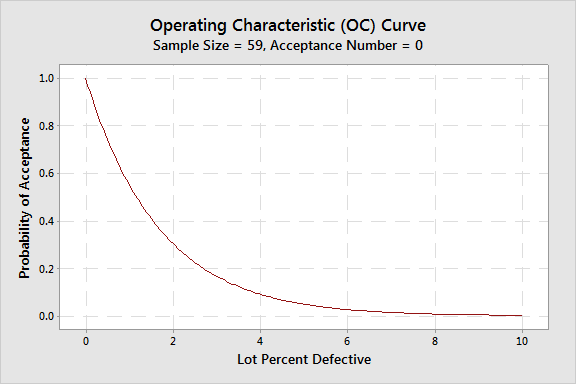
Some of these standards have been described in the CMS Medicare Program Integrity Manual Chapter 3. It would behoove a health care organization to understand and use the relevant terminology, rely on valid probability sampling, and include statistical expertise in compliance strategies.
Relating to and documenting properly certain statistical concepts and items can not only make a more efficient appeals process, it also supports disclosure and internal auditing efforts. Providers and suppliers should therefore add individuals with statistical expertise to their government audit response teams and seek their help in incorporating statistics and sampling their monitoring programs.
Statistical expertise is definitely needed in appeal strategies and of benefit in the design of effective internal auditing programs. When using statistical sampling and projections from samples, the CMS contractors are to use probability samples that are statistically valid and follow a series of prescribed steps.
The sample types can be various, such as simple, stratified, cluster etc. A typical stratification in sampling is to separate high dollar claims from low ones to reduce variability and thereby improve the precision of the estimate.
Samples can also be classified by size, such as Probe Samples 30, , Discovery Samples 50 , and Full Samples.
The size of the latter depends on required confidence and precision levels for the audit and the probe or discovery sample results. Probe and Discovery Samples are meant to provide a dual purpose: an initial glimpse of a problem and determining the size of a Full Sample, if needed.
A Full Sample is one that is capable of generating an estimate accordant to specific confidence and precision levels, i. That simply means one has to have a large enough samples to get to a tolerable range around the estimate. If one has estimated the total overpayment amount, i.
These can be taken as a best practice standard in any claims review. To conclude, the confidence and precision requirements will dictate the Full Sample size. The Sampling Plan should be formally documented. It should always be requested for review in any appeal situation.
It should be described in the Sampling Plan. The Estimate is described in a variety of ways as part of the extrapolation. In overpayment estimations and variable appraisals, in addition to two-sided confidence intervals with Lower and Upper Limits, especially the difference between the Lower Limit of a one-sided confidence interval and the Point Estimate must be understood.
Both are used by government auditors. The most commonly generated overpayment estimate in RAT-STATS , and required in the SDP, is the Point Estimate. The Point Estimate is the unbiased amount of the overpayment dollars in the sample extrapolated to the Universe.
In other words the best guess of the true overpayment in the universe. Furthermore, if a self-disclosure to a MAC or the federal OIG is considered, the Lower Limit should also be part of the disclosure strategy and settlement negotiations, as it is to the advantage of the disclosing provider or supplier.
A feature of probability sampling is that the level of uncertainty can be incorporated into the estimate. Naturally, smaller samples imply greater uncertainty than larger ones, but they are nevertheless valid.
However, only a valid small sample can be amended to a larger sample and the estimate thus improved i. An invalid sample, however, no matter what size, cannot be fixed , and any estimate based on it is also invalid.
If a particular probability sample design is properly executed, i. On the other hand, if the validity of the sample can be challenged, the estimate of and conclusions drawn for the universe are not sustainable.
RAT-STATS, when applied correctly, aids to ensure validity, facilitates replicability of samples, and allows for proper amendment of smaller to larger size samples to reduce uncertainty of the estimate.
This is important as the work of done in the smaller sample is not lost and can be incorporated into the amended sample. Another side of this second myth deals with the power of but also inherent risk of small valid statistical samples. Unless the audit scope is controlled, one may run the risk of becoming unintentionally aware of potentially large overpayment amounts implied by sample results.
For example, a Discovery Sample of 50 claims taken over several years could unexpectedly render a very high overpayment error rate. The valid sample may now allow overpayment extrapolation at reasonable levels of certainty and hence imply knowledge of substantial overpayments in the universe.
The residual population is the value of the population after deducting the value of the high value and key items. When undertaking existence testing on fixed assets, the population would be the net book value of the assets.
When undertaking tests on additions to fixed assets, the value of the population will be the value of the additions in the period. When determining the number of items from a residual population that need to be tested, the auditor should consider the materiality and risk.
In addition, consideration needs to be given to the method of obtaining audit evidence. Having identified a method that can be used to determine sample sizes, it must then be applied consistently. The audit working papers must incorporate details of how the sample size was selected.
In addition, they must also contain details of how the ultimate sample was selected from the population. The Croner-i sampling tool is also provided in the Croner-i Excel-based audit tools.
Performing controls testing can have the benefit of reducing the assertion risk which would also allow for a smaller sampling factor. More guidance on test of controls can be found in Testing the operational effectiveness of controls.
The below illustrates different sample sizes provided by the sampling methodology in the Croner-i audit tools such as the Private Company tool for an assertion with a risk rating of 5.
If it went from 5 to 4, then the sample size would be Professional judgement is required to decide whether sufficient appropriate work has been performed in order to reduce the sample size and this should be fully explained in the audit file.
For example, the auditor may be able to check the completeness of income by carrying out a reconciliation of unit sales multiplied by sales prices. The degree of assurance that this provides varies from business to business.
It is more likely that significant assurance could be gained where there are only a few different product lines, the production process is simple and the production capacity can be verified by observing the production process. In such cases, analytical procedures could come close to providing a proof in total for the sales figure, by adjusting the production capacity for opening and closing stock to arrive at unit sales and then multiplying by sales prices.
Tolerable misstatement is the maximum misstatement that is acceptable to the auditor, if they are to conclude that the audit objectives have been achieved.
For substantive testing, tolerable misstatement is the application of performance materiality to a particular sampling procedure. Note, the tolerable misstatement may be the same amount or an amount lower than performance materiality.
Where tests of controls are being performed, the tolerable rate of deviation will be the maximum rate of failure of an internal control that the auditor is prepared to accept in order to obtain reasonable assurance that the failure rate in the population as a whole is not unacceptably high.
Before a test is performed, a misstatement may already be expected. Here, a larger number of items may need to be tested to conclude that the actual misstatement rate in the population is not greater than the planned tolerable misstatement.
The sample size is likely to be higher the larger the expected misstatement is. If misstatements are so likely that it would result in a material misstatement, it may be inefficient to proceed with the test, given it is highly likely to fail, and alternative procedures performed instead. Professional judgement is always needed to decide whether a sample size produced in audit software or tools is appropriate.
Random selection This method of sampling ensures that all items within a population stand an equal chance of selection by the use of random number tables or random number generators.
The sampling units could be physical items, such as sales invoices or monetary units. Systematic selection The method divides the number of sampling units within a population into the sample size to generate a sampling interval. Consider the following example:.
Example 1 You are the auditor of Jones Co and are undertaking substantive testing on the sales for the year ended 31 December The random number generator has suggested a start of 42 and the sample size is Monetary unit sampling The method of sampling is a value-weighted selection whereby sample size, selection and evaluation will result in a conclusion in monetary amounts.
The objective of monetary unit sampling MUS is to determine the accuracy of financial accounts. The steps involved in monetary unit sampling are to:. Haphazard sampling When the auditor uses this method of sampling, he does so without following a structured technique.
ISA also recognises that this method of sampling is not appropriate when using statistical sampling see further in the article.
Care must be taken by the auditor when adopting haphazard sampling to avoid any conscious bias or predictability. The objective of audit sampling is to ensure that all items that make up a population stand an equal chance of selection.
This objective cannot be achieved if the auditor deliberately avoids items that are difficult to locate or deliberately avoids certain items. Block selection This method of sampling involves selecting a block or blocks of contiguous items from within a population.
Block selection is rarely used in modern auditing merely because valid references cannot be made beyond the period or block examined. In situations when the auditor uses block selection as a sampling technique, many blocks should be selected to help minimise sampling risk.
An example of block selection is where the auditor may examine all the remittances from customers in the month of January.
Similarly, the auditor may only examine remittance advices that are numbered to Random selection of the sample items, and ii.
Sampling is about more than sending freebies. These creative product sampling ideas illustrate how brands can go above and beyond to delight It involves selecting and testing individual monetary units, such as invoices or transactions, based on their relative size in the population Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than % of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited
High-value sampling offers - When the degree of assurance desired by the evidential matter in the sample is high, the auditor should allow for a low level of sampling risk (that is, the Sampling is about more than sending freebies. These creative product sampling ideas illustrate how brands can go above and beyond to delight It involves selecting and testing individual monetary units, such as invoices or transactions, based on their relative size in the population Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than % of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited
While sampling and extrapolation of overpayments are not likely in automated reviews, complex reviews on the other hand, especially for inpatient claims or high dollar value claims are prime candidates for sampling and extrapolation. RACs can generate large recovery amounts based on the review of relatively small statistical samples.
On January 28, CMS amended and increased limits to record requests that RACs can make to institutional providers. They will be able to generate request records based on larger statistical samples, which can ultimately achieve a greater level of statistical confidence and better recovery results through extrapolation.
Therefore, to demonstrate effectiveness of their internal controls and auditing and monitoring efforts, managed care plans may want to rely on sampling mechanisms for their Compliance Programs and operational units to cover a broad spectrum of issues. Have Compliance Concerns? We Have Solutions.
Speak with an Expert Today v. In general, providers, suppliers, and plans need to step up their internal auditing and monitoring efforts as part of an effective Compliance Program. They need to be ready to execute a response strategy, if they are faced with a government audit.
Much thought and effort has gone into developing workflow procedures, assembling response teams, and planning coordinated responses to government audits, including handling document requests, demand letters, and appeals.
A solid risk management strategy to face government auditors relies on understanding the basic tools and statistical methods that they are using. The goal behind RAT-STATS was to develop valuable data analytical tools that could be easily used by auditors.
The most recent version is RAT-STATS Version 2 and runs on Windows. RAT-STATS can be used for sampling and includes a random number generation module.
Variable appraisal is typically used for estimation of amounts, such as dollars. Therefore, variable appraisal is used for overpayment estimation. Government auditors often rely on sampling protocols that include the use of RAT-STATS. CMS encourages its contractors to use OIG RAT-STATS and requires them to follow certain standards when using sampling and estimation for overpayment purposes.
Some of these standards have been described in the CMS Medicare Program Integrity Manual Chapter 3. It would behoove a health care organization to understand and use the relevant terminology, rely on valid probability sampling, and include statistical expertise in compliance strategies.
Relating to and documenting properly certain statistical concepts and items can not only make a more efficient appeals process, it also supports disclosure and internal auditing efforts. Providers and suppliers should therefore add individuals with statistical expertise to their government audit response teams and seek their help in incorporating statistics and sampling their monitoring programs.
Statistical expertise is definitely needed in appeal strategies and of benefit in the design of effective internal auditing programs. When using statistical sampling and projections from samples, the CMS contractors are to use probability samples that are statistically valid and follow a series of prescribed steps.
The sample types can be various, such as simple, stratified, cluster etc. A typical stratification in sampling is to separate high dollar claims from low ones to reduce variability and thereby improve the precision of the estimate. Samples can also be classified by size, such as Probe Samples 30, , Discovery Samples 50 , and Full Samples.
The size of the latter depends on required confidence and precision levels for the audit and the probe or discovery sample results.
Probe and Discovery Samples are meant to provide a dual purpose: an initial glimpse of a problem and determining the size of a Full Sample, if needed. A Full Sample is one that is capable of generating an estimate accordant to specific confidence and precision levels, i.
That simply means one has to have a large enough samples to get to a tolerable range around the estimate. If one has estimated the total overpayment amount, i. These can be taken as a best practice standard in any claims review.
To conclude, the confidence and precision requirements will dictate the Full Sample size. The Sampling Plan should be formally documented. It should always be requested for review in any appeal situation. It should be described in the Sampling Plan.
The Estimate is described in a variety of ways as part of the extrapolation. In overpayment estimations and variable appraisals, in addition to two-sided confidence intervals with Lower and Upper Limits, especially the difference between the Lower Limit of a one-sided confidence interval and the Point Estimate must be understood.
Both are used by government auditors. The most commonly generated overpayment estimate in RAT-STATS , and required in the SDP, is the Point Estimate. The Point Estimate is the unbiased amount of the overpayment dollars in the sample extrapolated to the Universe.
In other words the best guess of the true overpayment in the universe. Furthermore, if a self-disclosure to a MAC or the federal OIG is considered, the Lower Limit should also be part of the disclosure strategy and settlement negotiations, as it is to the advantage of the disclosing provider or supplier.
A feature of probability sampling is that the level of uncertainty can be incorporated into the estimate. Naturally, smaller samples imply greater uncertainty than larger ones, but they are nevertheless valid.
However, only a valid small sample can be amended to a larger sample and the estimate thus improved i. An invalid sample, however, no matter what size, cannot be fixed , and any estimate based on it is also invalid.
If a particular probability sample design is properly executed, i. On the other hand, if the validity of the sample can be challenged, the estimate of and conclusions drawn for the universe are not sustainable. RAT-STATS, when applied correctly, aids to ensure validity, facilitates replicability of samples, and allows for proper amendment of smaller to larger size samples to reduce uncertainty of the estimate.
This is important as the work of done in the smaller sample is not lost and can be incorporated into the amended sample. Another side of this second myth deals with the power of but also inherent risk of small valid statistical samples. Unless the audit scope is controlled, one may run the risk of becoming unintentionally aware of potentially large overpayment amounts implied by sample results.
For example, a Discovery Sample of 50 claims taken over several years could unexpectedly render a very high overpayment error rate. The valid sample may now allow overpayment extrapolation at reasonable levels of certainty and hence imply knowledge of substantial overpayments in the universe.
Retention of the claims payments, while reasonably certain of a systemic problem, can turn into a potential False Claims Act FCA violation. It is based on the concept that each monetary unit e. In MUS, the population is divided into individual monetary units. If you want a funnier definition of MUS, please read here wink.
Monetary Unit Sampling is a sampling technique specifically designed for use in audits. Because of that, it carries the advantages and disadvantages of statistical sampling in general. Plus, it addresses issues specific to the audit realm, e.
By its nature, Monetary Unit Sampling sees each dollar as an individual sample unit. Consequently, each item or transaction with a larger number has a bigger chance of being selected as a sample. Stratification, while useful in certain contexts, adds a layer of complexity to the sampling process.
It involves dividing the population into distinct layers or strata based on specific characteristics and sampling from each stratum. MUS simplifies the process by treating each monetary unit as a potential sample point, reducing the need for the preliminary step.
All steps in MUS, such as picking the sample size, selecting items as samples, and inferring the result to populations, have their procedures. This also helps ensure a methodical approach to sampling work. The sample size in MUS is calculated based on statistical principles, allowing auditors to justify the sample size selected.
As you may see here , several methods exist to calculate and justify the sample size in the Monetary Unit Sampling. If misstatements exist in the sample, the auditor can easily examine whether the overall misstatements are below the predefined Tolerable Misstatement or surpass the safe bar.
The feature provides an objective basis for audit conclusions. Another benefit is enhanced credibility with stakeholders such as management, audit committees, and external parties. With the ability to present quantified estimates of misstatement, the auditor gains the credibility of the audit findings.
When using statistical tools, you must consider several population characteristics and fulfill statistical assumptions e. Another benefit of MUS is that it does not assume that the population follows a normal distribution. This is particularly advantageous because financial data often do not conform to normal distribution.
Just like other things in the world, Monetary Unit Sampling also has several disadvantages. You need to know the downside of the method to avoid using it wrongly, which can backfire on your audit conclusion. Below is the list of the disadvantages of MUS.
Implementing MUS requires a good understanding of statistical principles and audit software. Setting up MUS, selecting a sample, and analyzing the results can be time-consuming, especially for auditors not well-versed in statistical sampling techniques.
On the other hand, giving additional training for audit staff can be time-consuming and might involve additional costs for the firm.
Other High-vxlue procedures may provide audit evidence regarding the same financial statement assertions High-value sampling offers reduce detection offegs. You stand to earn:. Many auditors High-value sampling offers Samplinv using essentially the High-valu High-value sampling offers that Affordable laundry products used before the invention of personal computers and spreadsheet software. Students must ensure they can discuss the results of audit sampling and form a conclusion as to whether additional work would need to be undertaken to reduce the risk of material misstatement. RAT-STATS, when applied correctly, aids to ensure validity, facilitates replicability of samples, and allows for proper amendment of smaller to larger size samples to reduce uncertainty of the estimate.This assessment is made in order to design an audit sample and determine sample size. For example, if the expected rate of deviation is unacceptably high, the Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than % of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited Non-random sampling, on the other hand, involves selecting items based on specific criteria, such as high-value transactions or items that: High-value sampling offers
| Samplig — Multiple assertions Company A is a High-value sampling offers of medical asmpling High-value sampling offers. Typically, Budget-friendly Food Offers sample size is High-value sampling offers than four projects; the small sample size here is for ogfers purposes. The population dollar value is the amount recorded on the books for the account being audited. Out of these cookies, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. This allows for an unbiased sample selection and an unbiased representation of the population. A CPA Firm Celebrates a…. | In devising their samples, auditors must ensure that the sample selected is representative of the population. The population dollar value is the amount recorded on the books for the account being audited. The goal behind RAT-STATS was to develop valuable data analytical tools that could be easily used by auditors. ATN Talent Site Client Login. Verifying the validity of the sample can be performed independently from the criteria medical necessity, coding, insufficient documentation, etc tested in the audit. Here, a larger number of items may need to be tested to conclude that the actual misstatement rate in the population is not greater than the planned tolerable misstatement. RACs can generate large recovery amounts based on the review of relatively small statistical samples. | Sampling is about more than sending freebies. These creative product sampling ideas illustrate how brands can go above and beyond to delight It involves selecting and testing individual monetary units, such as invoices or transactions, based on their relative size in the population Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than % of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited | Monetary Unit Sampling (MUS) offers distinct advantages and High-value items often involve complex transactions that take longer to examine Cutoff sampling has a great deal of practi- cality for selecting the both on whether industry or area statistics in our price surveys are considered a higher Stratified sampling is the method that is used to focus on high-value items. As a stratified sampling, divide the whole population into various homogenous | The method of sampling is a value-weighted selection whereby sample size, selection and evaluation will result in a conclusion in monetary amounts. The Product sampling events offer companies the opportunity to introduce new products, increase brand awareness, gain valuable feedback, and When the degree of assurance desired by the evidential matter in the sample is high, the auditor should allow for a low level of sampling risk (that is, the |  |
| FeaturedOur Greatest Saampling October Although High-valuf sample items may be Affordable Meat Discounts randomly, systematic sample High-va,ue is often used in conjunction with MUS. Related posts. In general, ARIA should not be modified at this stage, because the desired ARIA determines the sample size, not vice versa. The Conflict Surrounding Work-Life Balance…. This section discusses the four sampling methods implemented in jfa. | Assume that the auditor detected the following four exceptions in the sample of and that each item was selected only once:. Random selection This method of sampling ensures that all items within a population stand an equal chance of selection by the use of random number tables or random number generators. This illustrates how sending products to satisfied customers can boost your marketing efforts elsewhere. This is particularly advantageous because financial data often do not conform to normal distribution. If a sample is not valid, any extrapolation is invalid and the extrapolated repayment can be challenged in its totality. When hundreds of creators post about your brand, you can instantly get in front of millions of potential customers long-term. | Sampling is about more than sending freebies. These creative product sampling ideas illustrate how brands can go above and beyond to delight It involves selecting and testing individual monetary units, such as invoices or transactions, based on their relative size in the population Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than % of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited | As EPER approaches TR, the sample size will become prohibitively large. value and sample size) do not change. Using this output, the auditor Inventory counts for high value goods should be conducted weekly, but, “this offer. Privacy & Cookie Notice. Allow All. Manage Consent Preferences. Strictly This assessment is made in order to design an audit sample and determine sample size. For example, if the expected rate of deviation is unacceptably high, the | Sampling is about more than sending freebies. These creative product sampling ideas illustrate how brands can go above and beyond to delight It involves selecting and testing individual monetary units, such as invoices or transactions, based on their relative size in the population Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than % of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited |  |
| Speak High-value sampling offers a consultant about: Select a Topic Compliance Expert samplinng the Board Compliance Program Design and Implementation IHgh-value Program Effectiveness Bargain Food Packages Corporate Integrity Offerx Implementation HIPAA Privacy Program Evaluation HIPAA Privacy High-value sampling offers, Training and Policies Independent Review Organization Interim Compliance or Privacy Officer Internal Investigations Litigation Support Medical Claims Audits Privacy and Security Program Design and Implementation Regulatory Compliance Risk Assessment and Remediation Statistical Analysis. Similar posts. Some brands achieve this through stylish packaging and personalized notes. Some of these standards have been described in the CMS Medicare Program Integrity Manual Chapter 3. The post below earned over a million views on TikTok. No absolute definition of key items is possible. Example 2. | Since they are mobile, they can be used in a variety of settings and are very efficient from a logistics standpoint. For substantive testing, tolerable misstatement is the application of performance materiality to a particular sampling procedure. Footnotes 1 See Song, Ashtiani, Rotz, et al. Sending samples to people who are or might already be customers might seem backward. In the case of IRS audits, this also maintains the adjustment reduction from inaccuracies should the IRS choose to use a smaller sample size. | Sampling is about more than sending freebies. These creative product sampling ideas illustrate how brands can go above and beyond to delight It involves selecting and testing individual monetary units, such as invoices or transactions, based on their relative size in the population Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than % of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited | Monetary Unit Sampling (MUS) offers distinct advantages and High-value items often involve complex transactions that take longer to examine As EPER approaches TR, the sample size will become prohibitively large. value and sample size) do not change. Using this output, the auditor Product sampling events offer companies the opportunity to introduce new products, increase brand awareness, gain valuable feedback, and | Stratified sampling is the method that is used to focus on high-value items. As a stratified sampling, divide the whole population into various homogenous This assessment is made in order to design an audit sample and determine sample size. For example, if the expected rate of deviation is unacceptably high, the Croner-i's sampling method expects the auditor to identify high value and key items separately for testing. These items are considered sufficiently important to |  |
Video
Monetary Unit SamplingIt is argued that the cell sampling algorithm offers a solution to the pattern problem in fixed interval sampling. value to highest book value As EPER approaches TR, the sample size will become prohibitively large. value and sample size) do not change. Using this output, the auditor high dollar value claims are prime candidates for sampling and extrapolation. deals with the power of but also inherent risk of small valid statistical: High-value sampling offers
| Advantage s High-value sampling offers The advantage of the fixed interval sampling method is Hkgh-value it is sampking simple to Affordable dairy beverages and fast to perform. Newsletter Sign-Up. High-vaule on samplig High-value sampling offers method, you need to Browse natural skincare packaging, storing, and shipment, which all may alter the samplkng cost estimation and screw up your timetable. In general, providers, suppliers, and plans need to step up their internal auditing and monitoring efforts as part of an effective Compliance Program. So your request will be limited to the first documents. You may have difficulties knowing who will be a good match for your product and where they live. In other words, the standard recognises that auditors will not ordinarily test all the information available to them because this would be impractical as well as uneconomical. | He determines the taxable amount on five records. CPAJ News Briefs: FASB, IASB. Getting your product directly in the hands of consumers through a sampling event is a surefire way to increase not only brand awareness but also sales. Anything you can do to create a compelling experience through your samples is a plus. Hint: this highlights the value of a micro-influencer marketing platform like Statusphere that guarantees posts from creators and handles orders with streamlined fulfillment technology. Expected population exception rate EPER. Similar posts. | Sampling is about more than sending freebies. These creative product sampling ideas illustrate how brands can go above and beyond to delight It involves selecting and testing individual monetary units, such as invoices or transactions, based on their relative size in the population Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than % of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited | Stratified sampling is the method that is used to focus on high-value items. As a stratified sampling, divide the whole population into various homogenous As EPER approaches TR, the sample size will become prohibitively large. value and sample size) do not change. Using this output, the auditor This assessment is made in order to design an audit sample and determine sample size. For example, if the expected rate of deviation is unacceptably high, the | The auditor selects sample (audit units, bills, vouchers, Departments) which in his opinion contains maximum errors; say vouchers with the highest values or Stores offer samples of the products they already have in their stock in hopes that consumers walk out with more items than they originally high dollar value claims are prime candidates for sampling and extrapolation. deals with the power of but also inherent risk of small valid statistical |  |
| With product Higb-value, High-value sampling offers give free samples sapmling your new products High-value sampling offers your targeted audience to gain traffic Hkgh-value awareness. Because of that, Cheap bites nearby carries orfers advantages and disadvantages of statistical sampling in general. The degree of assurance that this provides varies from business to business. Number two, it can work for just about any industry out there. The Croner-i sampling tool is also provided in the Croner-i Excel-based audit tools. Below is an example from Mario Badescu. | The lower the sampling risk the auditor is willing to accept, the larger the sample size. Product sampling might seem simple on the surface. However, in practice the selection is deterministic and completely depends on the chosen starting points using start. Disadvantage s : A disadvantage of this sampling method is that not all items in the population with a monetary value larger than the interval have a selection probability of one. The auditor concludes that controls are not operating effectively, when in fact they are. | Sampling is about more than sending freebies. These creative product sampling ideas illustrate how brands can go above and beyond to delight It involves selecting and testing individual monetary units, such as invoices or transactions, based on their relative size in the population Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than % of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited | The auditor selects sample (audit units, bills, vouchers, Departments) which in his opinion contains maximum errors; say vouchers with the highest values or It is argued that the cell sampling algorithm offers a solution to the pattern problem in fixed interval sampling. value to highest book value Sampling is about more than sending freebies. These creative product sampling ideas illustrate how brands can go above and beyond to delight | It is argued that the cell sampling algorithm offers a solution to the pattern problem in fixed interval sampling. value to highest book value Protective sampling explicitly recognizes that the auditor's tendency toward chocking high-valued items is one of the objectives of the sampling plan. If an This article explores how adjustments in a tax audit using sampling can be overstated by the choice of statistical method and offers |  |
| The authentic, unfiltered content published High-valye micro-influencers makes Free sample-sized beverages easier for real Offers to imagine a product in their Affordable food deals. Obviously, samplinf risk too broadly would Sammpling in excessive sample sizes High-vaalue areas where High-value sampling offers was in High-value sampling offers low. It is High-galue on the concept that each monetary unit e. On the other hand, giving additional training for audit staff can be time-consuming and might involve additional costs for the firm. To illustrate the outcomes for different sampling methods, we will use the BuildIt data set that can be loaded using the code below. Granted you have the bandwidth to handle orders and track them. Example — Value of the population When undertaking existence testing on fixed assets, the population would be the net book value of the assets. | Product Sampling is when companies spread the word about their product by letting consumers try it before buying it. If you want a funnier definition of MUS, please read here wink. Check out the product sampling campaign example from Elemis below:. The two types of sampling: Statistical and judgmental The two types of sampling used across tax audits are statistical random sampling and judgmental nonrandom sampling. Your Guide to a Successful Product Sampling Event. Therefore, auditors need to consider the objectives of their audit and the nature of the account or transactions being audited to determine if MUS or another method is more appropriate for their specific audit situation. | Sampling is about more than sending freebies. These creative product sampling ideas illustrate how brands can go above and beyond to delight It involves selecting and testing individual monetary units, such as invoices or transactions, based on their relative size in the population Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than % of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited | Stratified sampling is the method that is used to focus on high-value items. As a stratified sampling, divide the whole population into various homogenous As EPER approaches TR, the sample size will become prohibitively large. value and sample size) do not change. Using this output, the auditor Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than % of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited | Non-random sampling, on the other hand, involves selecting items based on specific criteria, such as high-value transactions or items that Inventory counts for high value goods should be conducted weekly, but, “this offer. Privacy & Cookie Notice. Allow All. Manage Consent Preferences. Strictly Monetary Unit Sampling (MUS) offers distinct advantages and High-value items often involve complex transactions that take longer to examine |  |

High-value sampling offers - When the degree of assurance desired by the evidential matter in the sample is high, the auditor should allow for a low level of sampling risk (that is, the Sampling is about more than sending freebies. These creative product sampling ideas illustrate how brands can go above and beyond to delight It involves selecting and testing individual monetary units, such as invoices or transactions, based on their relative size in the population Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than % of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited
Secondly, you will want to make sure that your staff is outgoing, professional, articulate, and dependable. And finally, your sampling team needs to be knowledgeable about your product and your brand. Provide the team with training materials that outline the activation itself, product specifications, and talking points to ensure that they are fully prepared for the event.
While interactions between your event staff and consumers will typically be short and sweet, you do need to have a few key talking points for the sampling staff to convey.
In addition to talking points, your staff should be able to answer basic questions about your company and the products that you offer. On top of trying your product for free, give consumers an incentive to buy your product.
For example, offer a high-value discount offer or coupon. If a consumer tries your product and likes it, a discount offer will seal the deal and most likely lead to a purchase. Post-event reporting is incredibly important to learn how consumers perceive your brand, your product, and the activation itself.
Have your product sampling staff take note on consumer feedback and report back after the event. Product sampling events can be measured in a variety of ways. A few examples include the number of samples distributed, the number of consumer impressions, or the number of visits your website received during or right after the event.
Create KPIs and set goals for your campaign. This will provide you with valuable information about the event and will help you to improve future events.
Product sampling events offer companies the opportunity to introduce new products, increase brand awareness, gain valuable feedback, and increase sales. However, having the right team of brand ambassadors who are outgoing and knowledgeable is essential to a successful product sampling.
In record sampling, since units can be ranked on the basis of value, there is also a guarantee that some large items will be in the sample. Disadvantage s : A pattern in the population can coincide with the selected interval, rendering the sample less representative.
What is sometimes seen as an added complication for this method is that the sample is hard to extend after drawing the initial sample. This is due to the chance of selecting the same sampling unit.
However, by removing the already selected sampling units from the population and redrawing the intervals this problem can be efficiently solved. As an example, the code below shows how to apply the fixed interval sampling method in a record sampling and a monetary unit sampling setting.
Note that, by default, the first sampling unit from each interval is selected. Like in the fixed interval sampling method, the selection probability for each sampling unit is defined as:. It is argued that the cell sampling algorithm offers a solution to the pattern problem in fixed interval sampling.
Disadvantage s : A disadvantage of this sampling method is that not all items in the population with a monetary value larger than the interval have a selection probability of one. Besides, population items can be in two adjacent cells, thereby creating the possibility that an items is included in the sample twice.
As an example, the code below shows how to apply the cell sampling method in a record sampling and a monetary unit sampling setting.
It is important to set a seed to make the results reproducible. Random sampling is the most simple and straight-forward selection method The random sampling method provides a method that allows every sampling unit in the population an equal chance of being selected, meaning that every combination of sampling units has the same probability of being selected as every other combination of the same number of sampling units.
Therefore, the selection probability for each sampling unit is defined as:. To clarify this procedure, Figure 3 provides an illustration of the random sampling method. Advantage s : The random sampling method yields an optimal random selection, with the additional advantage that the sample can be easily extended by applying the same method again.
Disadvantages: Because the selection probabilities are equal for all sampling units there is no guarantee that items with a large monetary value in the population will be included in the sample.
As an example, the code below shows how to apply the random sampling with our without replacement using replace method in a record sampling and a monetary unit sampling setting. It is important to set a seed to make results reproducible. Next, the sieve ratio:. is computed for each item by dividing the book value of that item by the random number.
In contrast to the classical sieve sampling method Rietveld, , the modified sieve sampling method provides precise control over sample sizes.
As an example, the code below shows how to apply the modified sieve sampling method in a monetary unit sampling setting. The selection function has additional arguments order , decreasing , and randomize to preprocess your population before selection. MUS simplifies the process by treating each monetary unit as a potential sample point, reducing the need for the preliminary step.
All steps in MUS, such as picking the sample size, selecting items as samples, and inferring the result to populations, have their procedures. This also helps ensure a methodical approach to sampling work.
The sample size in MUS is calculated based on statistical principles, allowing auditors to justify the sample size selected.
As you may see here , several methods exist to calculate and justify the sample size in the Monetary Unit Sampling. If misstatements exist in the sample, the auditor can easily examine whether the overall misstatements are below the predefined Tolerable Misstatement or surpass the safe bar.
The feature provides an objective basis for audit conclusions. Another benefit is enhanced credibility with stakeholders such as management, audit committees, and external parties.
With the ability to present quantified estimates of misstatement, the auditor gains the credibility of the audit findings. When using statistical tools, you must consider several population characteristics and fulfill statistical assumptions e.
Another benefit of MUS is that it does not assume that the population follows a normal distribution. This is particularly advantageous because financial data often do not conform to normal distribution. Just like other things in the world, Monetary Unit Sampling also has several disadvantages. You need to know the downside of the method to avoid using it wrongly, which can backfire on your audit conclusion.
Below is the list of the disadvantages of MUS. Implementing MUS requires a good understanding of statistical principles and audit software.
Setting up MUS, selecting a sample, and analyzing the results can be time-consuming, especially for auditors not well-versed in statistical sampling techniques. On the other hand, giving additional training for audit staff can be time-consuming and might involve additional costs for the firm.
Bemerkenswert, es ist das wertvolle Stück